Newton’s third law of motion — that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction — would appear to apply to the coal seam gas industry in Australia. The dramatic expansion of the industry in recent years has been matched by the community’s equally dramatic mobilisation against it. As my previous post showed, there are literally dozens of organisations on the web (and probably even more on Facebook) concerned in some way with the impacts of coal seam gas development. Some of these are well-established groups that have incorporated coal seam gas into their existing agendas, but many others seem to have popped up out of nowhere.
Most of these groups could be classified as community organisations insofar as they are concerned with a specific region or locality. But to think of them all as ‘grassroots’ organsiations, each having emerged organically on its own accord, might be a mistake. As the website network in my last post suggests, many of these groups might better be thought of as ‘rhizomatic’ (or lateral) offshoots inspired by the Lock the Gate Alliance. Lock the Gate emerged in 2010 and quickly reconfigured the landscape of community opposition to coal seam gas. Its campaigns, strategies and symbolism provided a handy template upon which locally focussed organisations could form. You’ll be hard-pressed to find a community-based anti-CSG group without a link to Lock the Gate on their website.
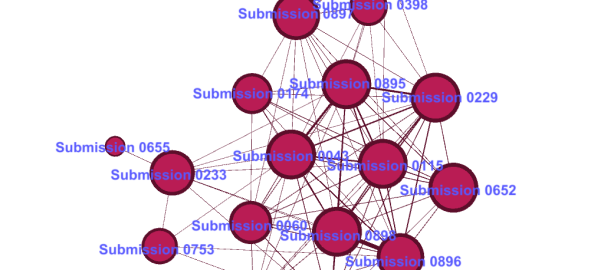
The lesson here is that voices that appear to be independent may to some extent be influenced or assisted by a small handful of highly motivated (or well resourced) groups or individuals. Having observed this possibility in the network of anti-CSG websites, I recently encountered it again while sifting through a very different dataset that I am preparing for textual analysis. The dataset in question is the 893 public submissions that the Parliament of New South Wales received in response to its 2011 inquiry into the environmental, health, economic and social impacts of coal seam gas activities. The submissions came from all kinds of stakeholders, including community groups, gas companies, scientific and legal experts, government agencies, and individual citizens. Of particular interest to me were the 660 submissions from individual citizens. Here was a sizable repository of views expressed straight from the minds and hearts of individual people, undistorted by the effects of groupthink or coordinated campaigns. Or so I thought. Continue reading Using Junk words to find recycled text